Gutenborn, Germany (September 10, 2014) – Brackish water shrimps belonging to the family Penaeidae are a highly valuable food commodity. Although shrimps contributed only 6.5% to the total world aquaculture production by quantity, they represented 14% of the value of aquaculture products in 2012. An increasing demand, limited production volumes and rising shrimp prices are responsible for this trend. One of the main obstacles in shrimp production are disease problems, which regularly lead to higher mortality rates and production losses. Measures of disease control, stabilization of the immune system and improving the health status of the shrimps have been focused in former investigations.
The reduction of antibiotics and other chemicals used in shrimp production is important for an environmentally sustainable development of the global aquaculture. Different feed additives, bioactive components and probiotics have been reported to support shrimp health and growth and have been discussed as an alternative for antibiotic use. Feed additives like vitamins, minerals or plant compounds are well known for their positive effects and commonly used in shrimp aquaculture.
The objective of the trial what to evaluate the efficiency of functional feed Sanbio SANA added to normal diets for White Leg Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) fed compared to similar diets but without addition of Sanbio SANA. The trial was performed according to the Best Practice Guideline by targeting the sensitive parameter (mortality, weight gain, feed intake, feed conversion rate).
The SANBOS GmbH, in cooperation with local partners, conducted a tank feeding trial with White Leg Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). The objective of the trial was to demonstrate Shrimps growth and performance in fresh-water tanks with a partial replacement of feed by the functional feed supplement Sanbio SANA (aquaculture grade).
 |  |  |
1. Materials and methods
The feeding was kept unchanged for the entire experiment. The stocking densities during experiment was 200-300 Shrimps per m2.
The reference diet contained fish meal (40.3%), shrimp meal (10%), squid meal (6%), wheat (13.53%), wheat flour (25%), fish oil (2%), vitamin premix (1.5%), Lecithin (1%), salt (0.6%) and Cholesterol (0.07%).
Table 1. Formula for the standard fish feed used in the trial
| Treatment | Unit | Control | Sanbio SANA |
| Diet | Mixture | |
| Pellet size | µm | 700-144 |
| Moisture | % | 5.4 |
| Ash | % | 10.3 |
| Protein | % | 40.8 |
| Crudefiber | % | 2.3 |
| Fat | % | 7.6 |
| Fatty acids | ||
| C14:0 | % | 0.00 |
| C16:0 | % | 23.84 |
| C16:1 | % | 6.97 |
| C18:0 | % | 4.83 |
| C18:1 n9c | % | 19.25 |
| C18:2 n6c | % | 17.85 |
| C20:1 | % | 2.84 |
| C18:3 n3 | % | 2.84 |
| C20:2 | % | 2.85 |
| C22:1 n9 | % | 0.00 |
| C23:0 | % | 0.00 |
| C22:2 | % | 0.00 |
| C20:5 n3 | % | 8.62 |
| C22:6 n3 | % | 10.11 |
| Energy | MJ/kg | 18 |
| Energy | % | 100 |
| Sanbio SANA | kg ton-1 of diet % | 0 | 20 0 | 2 |
Table 2. Water parameter during experiment (p<0.05)
| Treatment | Unit | Control | Sanbio SANA |
| Oxygen | mg/L | 6.75 | 6.78 |
| pH | 7.86 | 7.75 | |
| Temperature | °C | 30.69 | 31.08 |
| Salinity | °/°° | 13.90 | 14.18 |
| Ammonia | mg/L | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Nitrite | mg/L | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| Nitrate | mg/L | 15.23 | 14.70 |
Table 3. Productive performance data
| Treatment | Unit | Control | Sanbio SANA | |
| Survival | % | 26.00 | 38.22 | +47.0% |
| Final biomass | g | 29.54 | 39.37 | +33.3% |
| Weight gain | g | 27.58 | 37.41 | +35.5% |
| SGR | %/d | 14.08 | 13.55 | -3.9% |
| FCR | 1.37 | 0.93 | -47.3% |
SGR: Specific growth rate [% d-1] = (final weight – initial weight) x t-1 x 100
FCR: Feed conversion ratio = feed consumed x weight gain-1.
2. Results
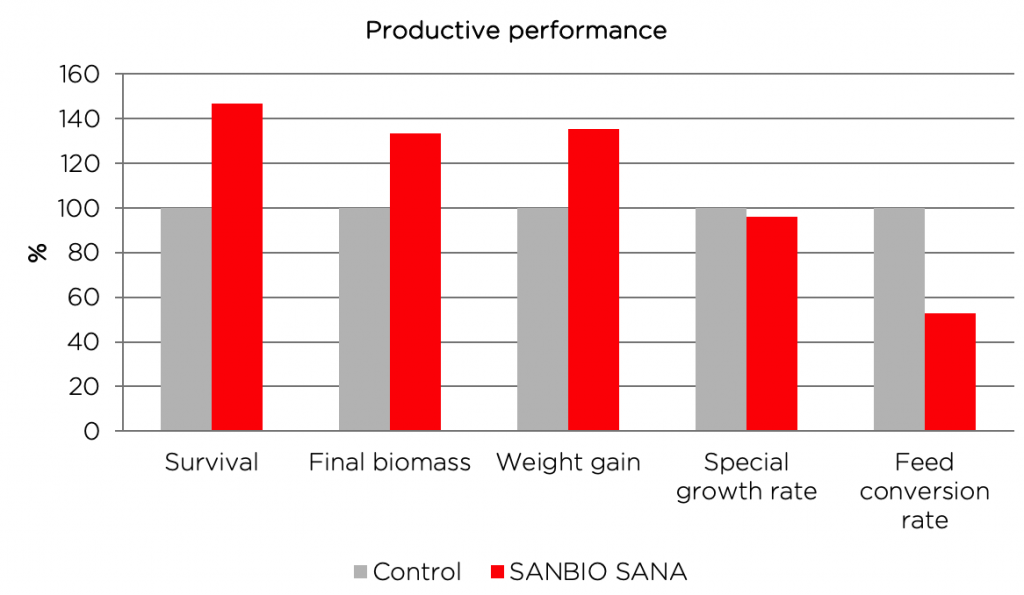
Figure 1. Productive performance in %
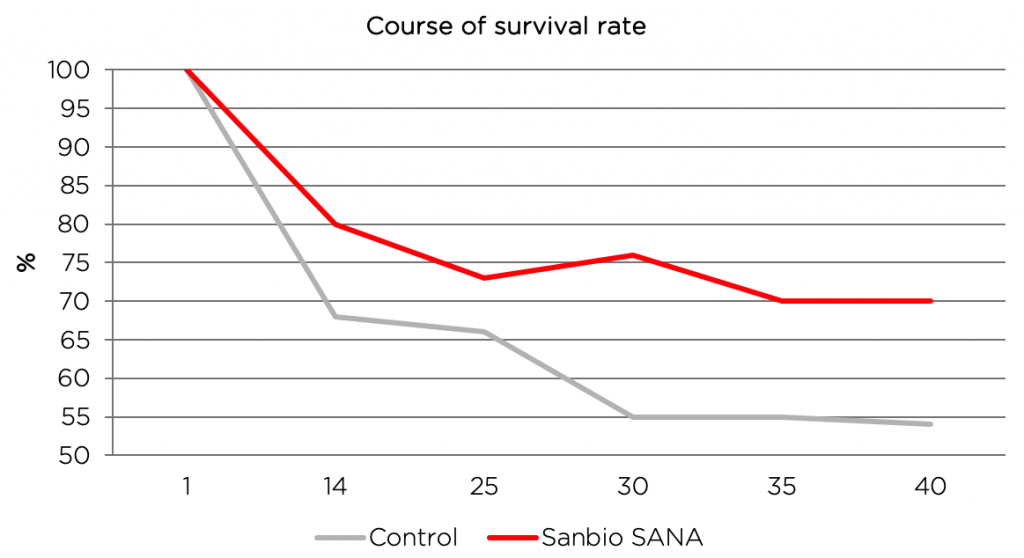
Figure 2. Course of survival rate during the trial period of 32 days in %
3. Conclusion
To summarize, the present study shows significantly positive effects of SANBIO SANA at the dosage of 2% of diet on productivity.
The positive effects at a glance:
- Highly absorption of mycotoxins of shrimp feed
- Improvement of health status
- Safety and tolerance when used dietary additions
- Increase of survival rate (even under high ammonia level)
- Increase of final biomass
- Improve of weight gain
- Improve of special growth rate
- Improved feed conversion rate.